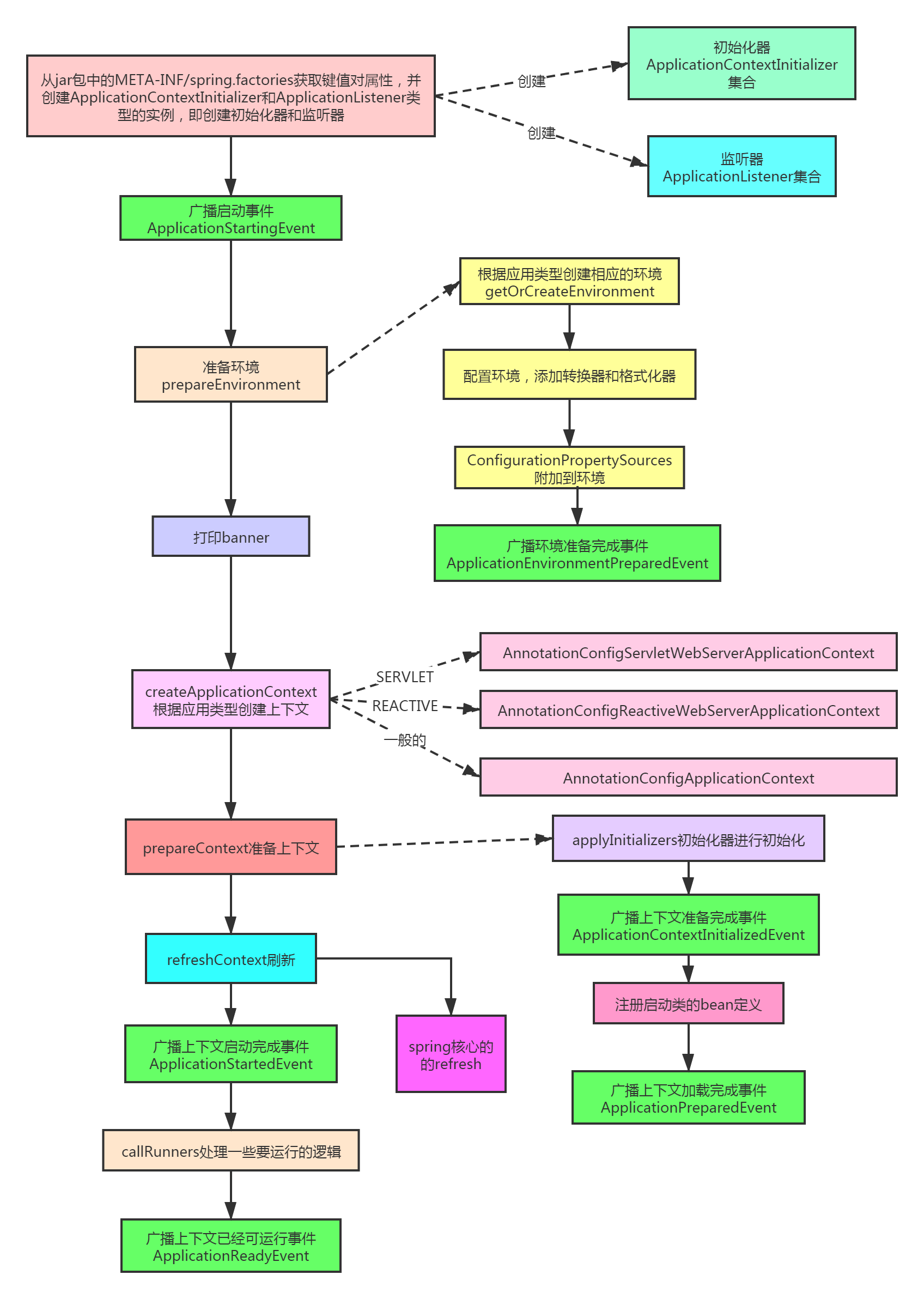
初始化基本流程
setInitializers设置初始化器
getSpringFactoriesInstances获取Spring工厂实例
SpringFactoriesLoader的loadFactoryNames
loadSpringFactories加载META-INF/spring.factories
PropertiesLoaderUtils的loadProperties加载资源文件
SpringApplication的createSpringFactoriesInstances创建相关类型的实例
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator的sort根据优先级排序
SpringApplication的setInitializers
初始化基本流程
getSpringFactoriesInstances(BootstrapRegistryInitializer.class))( 初始化引导注册表初始化器 ) 我们来看看这一句话做了什么:
1 this .bootstrapRegistryInitializers = new ArrayList <>( getSpringFactoriesInstances(BootstrapRegistryInitializer.class));
package org.springframework.boot;
回调接口,可用于在{@link BootstrapRegistry}使用前对其进行初始化。
/**
* Callback interface that can be used to initialize a {@link BootstrapRegistry} before it
* is used.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @since 2.4.5
* @see SpringApplication#addBootstrapRegistryInitializer(BootstrapRegistryInitializer)
* @see BootstrapRegistry
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BootstrapRegistryInitializer {
/**
* Initialize the given {@link BootstrapRegistry} with any required registrations.
* @param registry the registry to initialize
*/
void initialize(BootstrapRegistry registry);
}
给SpringApplication这个类的private final List<BootstrapRegistryInitializer> bootstrapRegistryInitializers;这个属性赋值,看看这个getSpringFactoriesInstances方法
实际是调用下面这个,SpringFactoriesLoader.forDefaultResourceLocation(getClassLoader()).load(type, argumentResolver);
forDefaultResourceLocation()方法注释是 创建一个 {@link SpringFactoriesLoader} 实例,该实例将加载并实例化来自{@value #FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION}的工厂实现,使用给定的类加载器
返回一个SpringFactoriesLoader对象,调用的是forResourceLocation,第一个参数是资源目录,资源目录是
这段代码的大概意思是从map缓存中获取SpringFactoriesLoader工厂实例, 如果指定的键(key)在映射中尚未关联值,则计算该键的值并将其存储在映射中。如果键已经存在,则直接返回现有的值,cache类型为 static final Map<ClassLoader, Map<String, SpringFactoriesLoader>> cache = new ConcurrentReferenceHashMap<>();先利用resourceClassLoader获取到 Map<String, SpringFactoriesLoader>类型的value,如果value有值的话就返回现在的值,没有的话 new ConcurrentReferenceHashMap<>()
1 2 return loaders.computeIfAbsent(resourceLocation, key -> new SpringFactoriesLoader (classLoader, loadFactoriesResource(resourceClassLoader, resourceLocation)));
这一步与上面类似,如果对应的key值有value的话就直接返回,没有的话new一个SpringFactoriesLoader,可以看到接收两个参数,一个classloader和一个loadFactoriesResource(resourceClassLoader, resourceLocation)),这个方法的具体方法内容为
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 protected static Map<String, List<String>> loadFactoriesResource (ClassLoader classLoader, String resourceLocation) { Map<String, List<String>> result = new LinkedHashMap <>(); try { Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader.getResources(resourceLocation); while (urls.hasMoreElements()) { UrlResource resource = new UrlResource (urls.nextElement()); Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); properties.forEach((name, value) -> { String[] factoryImplementationNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) value); List<String> implementations = result.computeIfAbsent(((String) name).trim(), key -> new ArrayList <>(factoryImplementationNames.length)); Arrays.stream(factoryImplementationNames).map(String::trim).forEach(implementations::add); }); } result.replaceAll(SpringFactoriesLoader::toDistinctUnmodifiableList); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Unable to load factories from location [" + resourceLocation + "]" , ex); } return Collections.unmodifiableMap(result); }
可以轻松看到这是加载springboot jar包下的spring.factories文件
最终结果为19条,但是springboot下面的spring.factories的文件只有15条,这是什么原因呢?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 # Logging Systems org.springframework.boot.logging.LoggingSystemFactory=\ org.springframework.boot.logging.logback.LogbackLoggingSystem.Factory,\ org.springframework.boot.logging.log4j2.Log4J2LoggingSystem.Factory,\ org.springframework.boot.logging.java.JavaLoggingSystem.Factory # PropertySource Loaders org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourceLoader=\ org.springframework.boot.env.PropertiesPropertySourceLoader,\ org.springframework.boot.env.YamlPropertySourceLoader # ConfigData Location Resolvers org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigDataLocationResolver=\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigTreeConfigDataLocationResolver,\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.StandardConfigDataLocationResolver # ConfigData Loaders org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigDataLoader=\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigTreeConfigDataLoader,\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.StandardConfigDataLoader # Application Context Factories org.springframework.boot.ApplicationContextFactory=\ org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.ReactiveWebServerApplicationContextFactory,\ org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContextFactory # Run Listeners org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=\ org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener # Error Reporters org.springframework.boot.SpringBootExceptionReporter=\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzers # Application Context Initializers org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\ org.springframework.boot.context.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer,\ org.springframework.boot.context.ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer,\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer,\ org.springframework.boot.rsocket.context.RSocketPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer,\ org.springframework.boot.web.context.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer # Application Listeners org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\ org.springframework.boot.ClearCachesApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextCloserApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.context.FileEncodingApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.AnsiOutputApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.context.logging.LoggingApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener # Environment Post Processors org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=\ org.springframework.boot.cloud.CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor,\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor,\ org.springframework.boot.env.RandomValuePropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor,\ org.springframework.boot.env.SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor,\ org.springframework.boot.env.SystemEnvironmentPropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor,\ org.springframework.boot.reactor.ReactorEnvironmentPostProcessor # Failure Analyzers org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzer=\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigDataNotFoundFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.context.properties.IncompatibleConfigurationFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.context.properties.NotConstructorBoundInjectionFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.AotInitializerNotFoundFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanCurrentlyInCreationFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanDefinitionOverrideFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanNotOfRequiredTypeFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BindFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BindValidationFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.InvalidConfigurationPropertyNameFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.InvalidConfigurationPropertyValueFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.MissingParameterNamesFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.MutuallyExclusiveConfigurationPropertiesFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.NoSuchMethodFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.PatternParseFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.PortInUseFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.UnboundConfigurationPropertyFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.ValidationExceptionFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.liquibase.LiquibaseChangelogMissingFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.web.context.MissingWebServerFactoryBeanFailureAnalyzer,\ org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.ConnectorStartFailureAnalyzer # Failure Analysis Reporters org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalysisReporter=\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.LoggingFailureAnalysisReporter # Database Initializer Detectors org.springframework.boot.sql.init.dependency.DatabaseInitializerDetector=\ org.springframework.boot.flyway.FlywayDatabaseInitializerDetector,\ org.springframework.boot.jdbc.init.DataSourceScriptDatabaseInitializerDetector,\ org.springframework.boot.liquibase.LiquibaseDatabaseInitializerDetector,\ org.springframework.boot.orm.jpa.JpaDatabaseInitializerDetector,\ org.springframework.boot.r2dbc.init.R2dbcScriptDatabaseInitializerDetector # Depends On Database Initialization Detectors org.springframework.boot.sql.init.dependency.DependsOnDatabaseInitializationDetector=\ org.springframework.boot.sql.init.dependency.AnnotationDependsOnDatabaseInitializationDetector,\ org.springframework.boot.jdbc.SpringJdbcDependsOnDatabaseInitializationDetector,\ org.springframework.boot.jooq.JooqDependsOnDatabaseInitializationDetector,\ org.springframework.boot.orm.jpa.JpaDependsOnDatabaseInitializationDetector # Resource Locator Protocol Resolvers org.springframework.core.io.ProtocolResolver=\ org.springframework.boot.io.Base64ProtocolResolver
回到源码debug一下,发现还加载了autoconfig(9条),aop(1条)
最终结果为19条,是因为去掉了重复项
获取到之后,调用load(type, argumentResolver);这个方法进去
调用load方法,大致说明是:/**
* 从{@value #FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION}加载并实例化给定类型的工厂实现,使用配置的类加载器和给定的参数解析器。
* <p>返回的工厂通过{@link AnnotationAwareOrderComparator}进行排序。
* <p>从Spring Framework 5.3开始,如果在给定的工厂类型中发现重复的实现类名,只会实例化一个重复实现类型的实例。
* @param factoryType 表示工厂的接口或抽象类
* @param argumentResolver 用于通过类型解析构造函数参数的策略
* @throws IllegalArgumentException 如果任何工厂实现类无法加载,或者在实例化任何工厂时发生错误
* @since 6.0
*/
依次调用上面几个方法,debug一下,这里是根据factoryType类型再次筛选,类型为getSpringFactoriesInstances(BootstrapRegistryInitializer.class))这里的BootstrapRegistryInitializer.class,具体筛选方法为loadFactory(),里面调用getOrDefault(),自己查看源码,不做赘述
我们通过main方法调用一下由于
由于我们没有实现给定的类型的类加载器,所以size为0;
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));( 设置应用上下文初始化器 ) 这个与上面类似,给private List<ApplicationContextInitializer<?>> initializers属性赋值,也是加载工厂,只不过类型为ApplicationContextInitializer<?>这个接口进去看一下
回调接口,用于在Spring的{@link ConfigurableApplicationContext}被{@linkplain ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh()刷新}之前进行初始化。
* <p>通常用于需要对应用程序上下文进行一些程序化初始化的Web应用程序。例如,对{@linkplain ConfigurableApplicationContext#getEnvironment()上下文的环境}注册属性源或激活配置文件。参见{@code ContextLoader}和{@code FrameworkServlet}支持声明"contextInitializerClasses"上下文参数和init-param。
* <p>鼓励{@code ApplicationContextInitializer}处理器检测是否实现了Spring的{@link org.springframework.core.Ordered Ordered}接口,或者是否存在{@link org.springframework.core.annotation.Order @Order}注解,并在调用前相应地对实例进行排序。
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 3.1
* @param <C> 应用程序上下文类型
* @see org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader#customizeContext
* @see org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader#CONTEXT_INITIALIZER_CLASSES_PARAM
* @see org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#setContextInitializerClasses
* @see org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#applyInitializers
执行过程与上面一样,只不是工厂接口不一样,不做赘述,我们也用main方法测试一下
这次运行有七个spring工厂实例
这里是对每个实例的简要说明:
1. `org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer@5622fdf`:
- 这个初始化器负责将Spring Boot的`ApplicationContext`代理给Spring的原生`ConfigurableApplicationContext`。这允许在Spring Boot应用中使用Spring框架的原生功能。
2. `org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer@4883b407`:
- 这个初始化器确保所有上下文共享同一个`MetadataReaderFactory`实例,这是Spring用来读取类元数据的工厂。
3. `org.springframework.boot.context.ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer@7d9d1a19`:
- 这个初始化器设置应用上下文的ID,通常是从`application.properties`或`application.yml`配置文件中读取的。
4. `org.springframework.boot.context.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer@39c0f4a`:
- 这个初始化器负责在启动时打印出关于配置问题的警告,例如不推荐的配置属性。
5. `org.springframework.boot.rsocket.context.RSocketPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer@1794d431`:
- 如果你的应用使用了Spring Boot的RSocket支持,这个初始化器会在启动时注册RSocket服务器的端口信息。
6. `org.springframework.boot.web.context.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer@42e26948`:
- 这个初始化器会在启动时注册Web服务器的端口信息,例如Tomcat的端口。
7. `org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.logging.ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener@57baeedf`:
- 这个监听器用于在启动时记录条件评估报告,这有助于调试自动配置的条件。
这些实例不是“奇怪”的,而是Spring Boot框架的一部分,它们在应用启动时提供了额外的初始化逻辑。这些初始化器和监听器通过`META-INF/spring.factories`文件注册,Spring Boot在启动时会自动加载它们。每个实例后面的`@xxxx`是对象的哈希码,用于唯一标识实例。
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));( 设置事件监听器 ) 事件监听器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 应用事件监听器需要实现的接口。 * <p>基于标准的{@link java.util.EventListener}接口,用于观察者设计模式。 * <p>{@code ApplicationListener}可以泛型声明它感兴趣的事件类型。当注册到Spring的{@code ApplicationContext}时,事件将相应地进行过滤,只有匹配的事件对象才会触发监听器的调用。 * @author Rod Johnson * @author Juergen Hoeller * @param <E> 要监听的特定{@code ApplicationEvent}子类的类型 * @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent * @see org.springframework.context.event.ApplicationEventMulticaster * @see org.springframework.context.event.SmartApplicationListener * @see org.springframework.context.event.GenericApplicationListener * @see org.springframework.context.event.EventListener
运行main方法看一下,有8个
1 2 3 4 5 List<ApplicationListener> load2 = SpringFactoriesLoader.forDefaultResourceLocation(loader).load(ApplicationListener.class, (SpringFactoriesLoader.ArgumentResolver) null ); for (ApplicationListener l:load2) { System.out.println(l.toString()); } System.out.println(load2.size());
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 这些是Spring Boot中实现`ApplicationListener`接口的事件监听器的实例,每个实例都用于处理Spring应用上下文中的不同事件。以下是每个监听器的简要说明: 1. `org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener@6325a3ee`: - 这个监听器用于在Spring环境准备完成后,但在应用上下文刷新之前,对环境进行额外的处理。 2. `org.springframework.boot.context.config.AnsiOutputApplicationListener@1d16f93d`: - 这个监听器处理ANSI输出设置,确保控制台输出的颜色和格式化在不同的操作系统上都能正确显示。 3. `org.springframework.boot.context.logging.LoggingApplicationListener@67b92f0a`: - 这个监听器用于在应用启动时初始化日志系统,并在应用关闭时清理日志系统。 4. `org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.BackgroundPreinitializer@2b9627bc`: - 这个监听器用于在Spring Boot应用启动前预初始化一些背景任务,以加快启动速度。 5. `org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationListener@65e2dbf3`: - 这个监听器可能是用于代理其他监听器的事件处理,以便在不同的上下文中应用相同的事件处理逻辑。 6. `org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextCloserApplicationListener@4f970963`: - 这个监听器确保在关闭子应用上下文时,其父上下文也会被正确关闭。 7. `org.springframework.boot.ClearCachesApplicationListener@61f8bee4`: - 这个监听器用于在应用上下文刷新后清除Spring框架内部的一些缓存,以减少内存占用。 8. `org.springframework.boot.context.FileEncodingApplicationListener@7b49cea0`: - 这个监听器用于设置文件编码,确保文件读写操作使用正确的字符编码。
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass(); 这里就是推断启动类的,直接抛出异常,然后找到 main方法所在的类, 用于推断Spring Boot应用的主程序类。这个方法会检查各种线索,如传递给 SpringApplication.run()方法的参数、应用的类路径等,以确定哪个类包含 main方法
1 2 3 4 5 private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass() { return StackWalker.getInstance(StackWalker.Option.RETAIN_CLASS_REFERENCE) .walk(this ::findMainClass) .orElse(null ); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 返回一个具有指定选项的`StackWalker`实例,该选项确定它可以访问的栈帧信息。 * <p> * 如果存在安全管理器,并且给定的`option`是{@link Option#RETAIN_CLASS_REFERENCE Option.RETAIN_CLASS_REFERENCE},它会调用其{@link SecurityManager#checkPermission checkPermission}方法,传入{@code RuntimePermission("getStackWalkerWithClassReference" )}。 * @param option 栈遍历选项{@link Option} * * @return 配置了给定选项的`StackWalker` * * @throws SecurityException 如果存在安全管理器,并且其`checkPermission`方法拒绝访问权限。 public static StackWalker getInstance (Option option) { return getInstance(EnumSet.of(Objects.requireNonNull(option))); } public static StackWalker getInstance (Set<Option> options) { if (options.isEmpty()) { return DEFAULT_WALKER; } EnumSet<Option> optionSet = toEnumSet(options); checkPermission(optionSet); return new StackWalker (optionSet); }